How to choose UPS

To independently search for suitable uninterruptible power supplies, you can use our convenient catalog with selection by parameters. Wide selection of compatible batteries is available at following link.
Choosing UPS for PC
Modern PCs are usually equipped with switching power supplies, so they can be considered relatively insensitive to current quality. In this regard, it is permissible to purchase low-cost “uninterruptible power supply” of backup type(we will talk more about the types of UPS later).
When choosing the power of model, you need to take into account the consumption of not only the system unit, but also other devices, including monitor and peripherals. Is the scanner and printer required to operate autonomously? Let’s say that if force majeure happens at home you can do without them, but for an office and especially copy center it’s unlikely.
 |
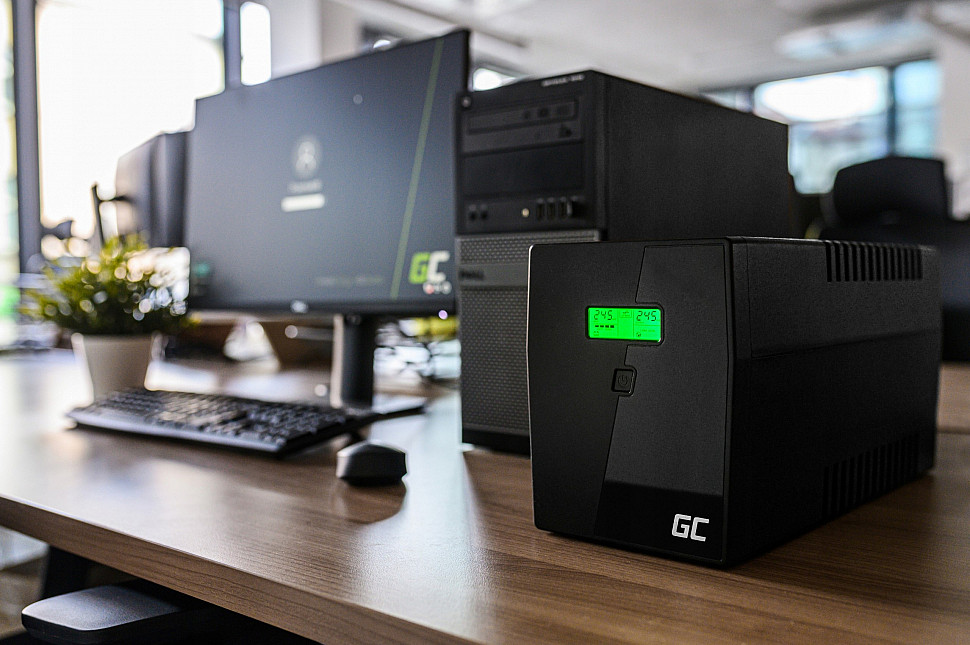
| For PCs, you can consider the simplest backup or interactive UPS. |
In the capacity of UPS for PC, it is worth including reserve of 20% and the same amount or at least 10% for the future (hardware update). For an office computer, 500 W model is usually sufficient, but for gaming machine, it is better to consider 1000 W options.
If the low-cost allows, then it is advisable to consider slightly more advanced interactive “uninterruptible power supply” systems. If you don’t want to overpay, then to extend the life of the backup UPS battery, it is recommended to purchase an inexpensive voltage stabilizer.
Deciding on UPS for refrigerator or freezer
Refrigerators and freezers are considered to be quite sensitive to power surges. Accordingly, to protect them and ensure autonomous operation, backup UPSs are not suitable - line-interactive or inverter UPSs are needed.
Another important requirement is the presence of pure sine wave. In short, refrigerators and freezers have compressor (actually motor), and if the input signal is incorrect (not an ideal sine wave), it is capable of working, but with overheating and the risk of accelerated wear.
 |
| To provide autonomous power to refrigerator without an inverter, you need very powerful UPS. |
The third important point when choosing is the correct calculation of power taking into account starting currents. Here you need to consider the type of device. If it is freezer or refrigerator with an inverter compressor, then there are either no large starting currents in it at all, or not much higher than typical energy consumption. Accordingly, you can limit yourself to an uninterruptible power supply of up to 500 W. If you have refrigerator with conventional compressor, then the inrush currents at startup exceed the average power consumption by 7 times. So, with value of 120 W, you need to have an 840 W UPS (and with reserve - all 1000 W), otherwise the device simply will not turn on.
The last significant aspect is battery capacity. It is recommended to equip UPS with battery of at least 50 Ah (at 12 V). By the way, in the event of power failure, it is not necessary to connect the refrigerator to the UPS immediately: if you do not open it, then the modern model keeps the cold well for over 10 hours. The exact value of autonomy is most often given in the instructions for the device.
Select UPS for gas boiler
Initially, it is necessary to make reservation that gas boilers without pump and electronics, as a rule, do not need uninterruptible power supplies at all, because they are non-volatile. But modern heating systems are usually based on devices with microcontrollers and circulation pumps. They are more efficient, but require power. Such gas boilers are demanding on signal quality, which means it is recommended to consider UPS with pure sine wave.
 |
| The electronics of gas boiler require pure sine wave. |
Another important factor is taking into account the phase dependence of the boiler. In short, some boiler devices require “through zero” and strict consideration of polarity. As rule, you can even use simple indicator screwdriver to check the “plus” and “minus”, both on the boiler and on UPS, and then make the correct connection. If you do not really understand what is said above, then it is better to invite an electrician to your home, who will perform simple manipulations while observing polarity and all safety rules.
The power consumption of modern gas boilers is low (about 100 W), although one of the elements of the system - the circulation pump - has increased starting currents. Usually the latter do not exceed 300 W. In general, 500 W UPS is sufficient for boiler. And with 100 Ah (12 V) battery, you can provide about 10 hours of uninterrupted operation.
By the way, if you have heated floor comb and there is pump, then it also needs to be autonomous. You will need separate UPS with pure sine wave, or you can take one more powerful “uninterruptible power supply” that will “pull” the entire heating system.
Choosing UPS for router or camera
Everything here is quite simple - for one low-voltage consumer it is advisable to take special UPS(aka mini UPS). These UPSs supply low voltage current (usually up to 18 V). As rule, only one device can be connected to them, for example, video surveillance camera or router. As a rule, for the latter, models with corresponding connector (and sometimes set of adapters) are offered. And for video surveillance systems there are solutions with terminal blocks.
Deciding on UPS for housing backup power
If you need to connect several devices to an uninterruptible power supply at once, for example, the same gas boiler, refrigerator, lighting, TV, other small gadgets, then you first need to calculate their total power consumption. Of course, everything depends on the specific use case, but, as rule, UPS with high effective power will be needed.
 |
| UPS for autonomy of an entire house is powerful device with an abundance of batteries. |
If you have at least one device sensitive to voltage quality, you should consider only models with pure sine wave. Another important point is sufficient number of sockets with backup.
In practice, the bottleneck of backup power supply systems with an abundance of “consumers” based on UPS is autonomy. In order to achieve even conventional 4 hours of operation of several devices when the lights are turned off, sometimes solid battery rack is required (see the calculation example below in the “Autonomy” section). This is not cheap pleasure, plus you also need to find suitable place for all this - preferably away from recreation areas.
But if UPSs for backup power are used in private homes or cottages, then it is not necessary to chase battery packs worth hundreds or even thousands of Ah. You can limit yourself to set of batteries for autonomy of couple of hours, and in case of longer force majeure, power the “uninterruptible power supply” from a gasoline generator. When you have high-quality online UPS, it is advisable to take fairly simple (asynchronous) but powerful device, rather than an inverter solution, because UPS easily converts “dirty current” into perfect sine wave at the output.
Separately, it is worth mentioning that for private home with an abundance of “consumers” or, say, for data center, it is advisable to consider three-phase “uninterruptible power supplies”. They can power not only refrigerator, an entrance gate, boiler and TV with lighting, but also, for example, powerful kitchen appliances. Although in general , single-phase solutions are usually chosen for domestic use.
If there is utmost clarity with UPS application scenarios, then various device parameters can be considered more specifically. By the way, it’s worth understanding the types and key technical aspects of uninterruptible power supplies even when you don’t fully understand why this equipment is needed.
UPS type or architecture
In accordance with the architecture (set of internal components and operating principles), there are three main types of UPS:
 |
| UPS paired with PC is usually needed to shut down the work correctly. |
- Backup or Off-line UPS. These are the simplest and often the most inexpensive models. Such UPSs do not have an input signal stabilizer, so they switch operation to the battery (battery) not only during emergency power outages, but also during power surges. As a result, if the power grid is unstable, the battery actively wears out and its service life decreases. The disadvantages of backup UPSs include not the fastest switching time (up to 20 ms) - this is usually enough for computer, but not for demanding equipment. At the output, such an “uninterruptible power supply” produces a modified sine wave, which also limits the scope of useful applications (more on this below). In general, backup UPSs are designed to work with undemanding equipment and devices that have switching power supplies (including most PCs, monitors, TVs, etc.). It is recommended to use Off-line UPS in stable power networks where there are no frequent power surges.
- Line-interactive or line-interactive UPS. The main difference between such “uninterruptible power supplies” is the presence of an input voltage stabilizer. Therefore, during surges, this UPS equalizes the power grid and does not switch to battery operation. Such models switch to battery power faster when the lights are turned off (usually in few ms), which makes them suitable choice for literally any PC, and often even for video surveillance systems(where speed also plays an important role). Interactive UPSs are more expensive than backup ones; they, as a rule, do not produce pure, but modified sine wave, which is not suitable for the most sensitive equipment, including audio equipment, boiler room automation, etc.
- Inverter or online UPS. These are the most progressive solutions today. Here, double current conversion is performed: first, the alternating current is transformed into direct current, and then again into an alternating current, but with an ideal sinusoid and voltage value of 230 V. There are no delays when switching to operation from the battery when the power supply is turned off. Inverter UPSs are suitable for the most demanding equipment, including ensuring the autonomous operation of complex server or medical equipment and other “picky consumers”. But the price for online UPS is the highest.
Sometimes so-called low-voltage models designed for routers and CCTV cameras are classified into separate category of “uninterruptible power supplies”.
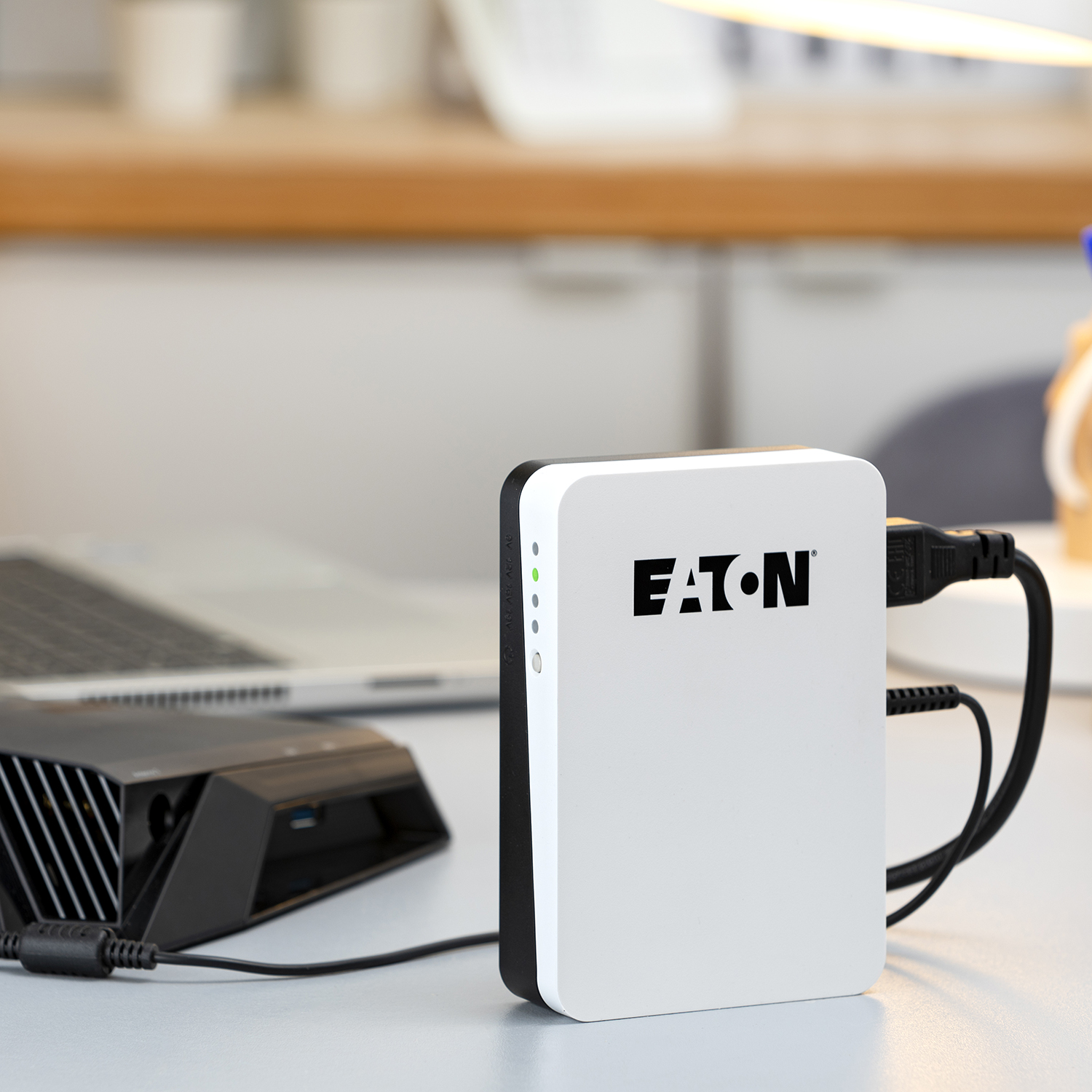 |
| Today, special UPSs are produced for routers and low-voltage equipment. |
Uninterruptible power supply power
When you already have an idea of the types of UPS, you can proceed to one of the defining selection criteria - power. Modern models often offer two power parameters, namely:
- the maximum output power, which is given in units such as VA, that is, in volt-amperes. To get real performance indicator, you need to use correction factor, which directly depends on the type of equipment connected and ranges from 0.7 to 0.95. Let’s say for telecommunications equipment, servers and PCs with power supplies with active PFC it is 0.95, for lighting - 0.9, and for household appliances with motors - about 0.7.
- effective power output. This is already value in the usual Watts. In fact, it already takes into account the main correction factors. And if it is indicated in the documentation or on the official website of UPS manufacturer, then you should immediately focus on it.
How to find out the UPS capacity for your needs? Approximate consumption figures for popular household appliances are shown in the table below:
For more accurate calculations, use the following recommendations:
- Determine the power values of the devices that you plan to connect to the uninterruptible power supply. If this is more than one device, then summarize the parameters.
- Allow reserve of at least 20%. Conventionally, if you get 500 W, then when choosing, you need to focus on at least 600 W.
- The resulting figure is the effective power output. But even if it is given by the manufacturer, do not rush to select model.
- For example, for personal computers it is additionally recommended to reserve about 20% for possible system update. This could be buying new video card or monitor with larger screen diagonal.
- For appliances with electric motors, and this includes wide variety of household appliances, including vacuum cleaners, washing machines, refrigerators, and food processors, you also need to take into account the value of starting currents. They are usually approximately 5 to 7 times higher than the power consumption. The UPS must cover this short-term surge.
Output voltage form
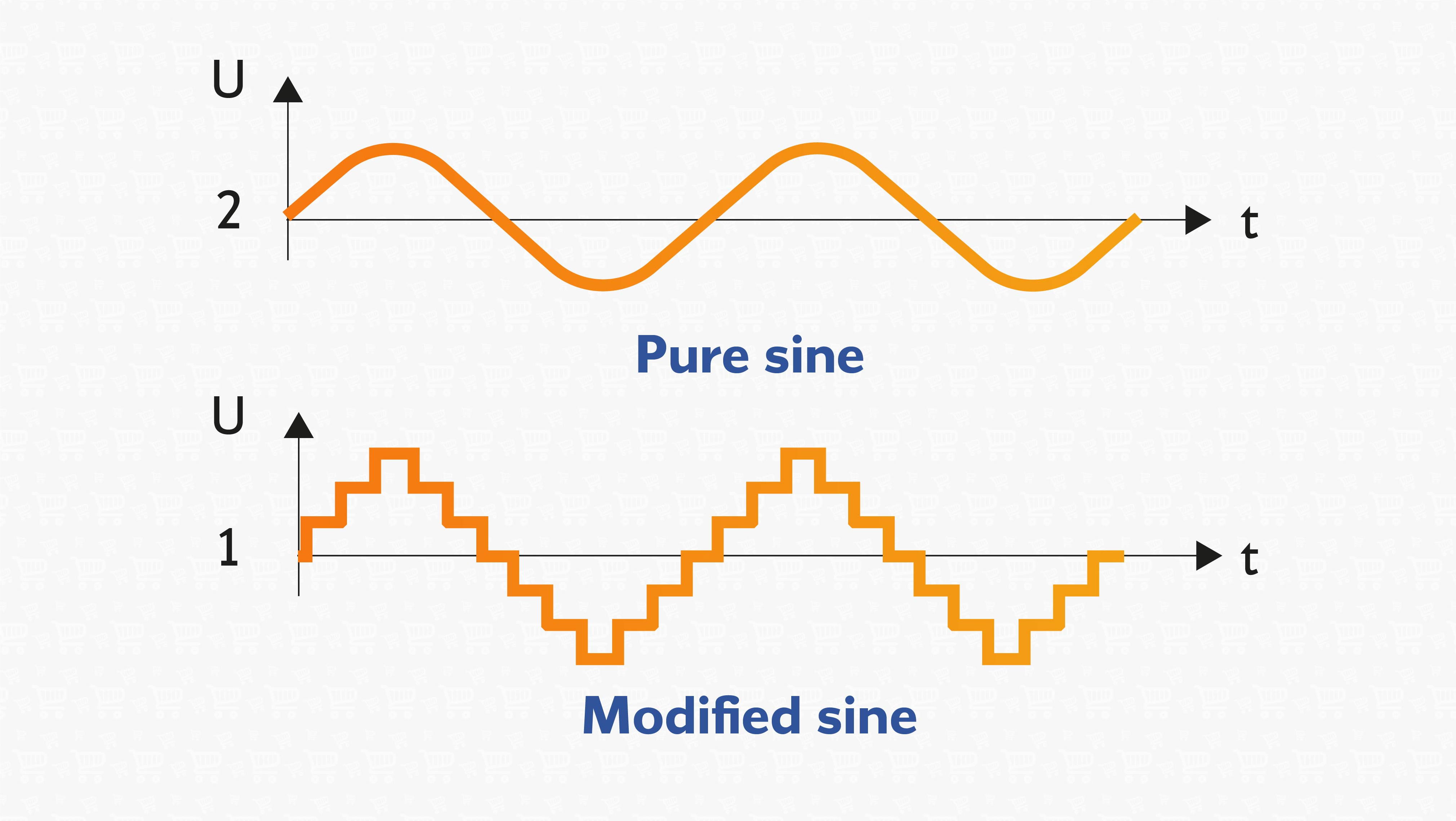
Another critical parameter for choosing an uninterruptible power supply is the type of output signal it provides. There are two main options:
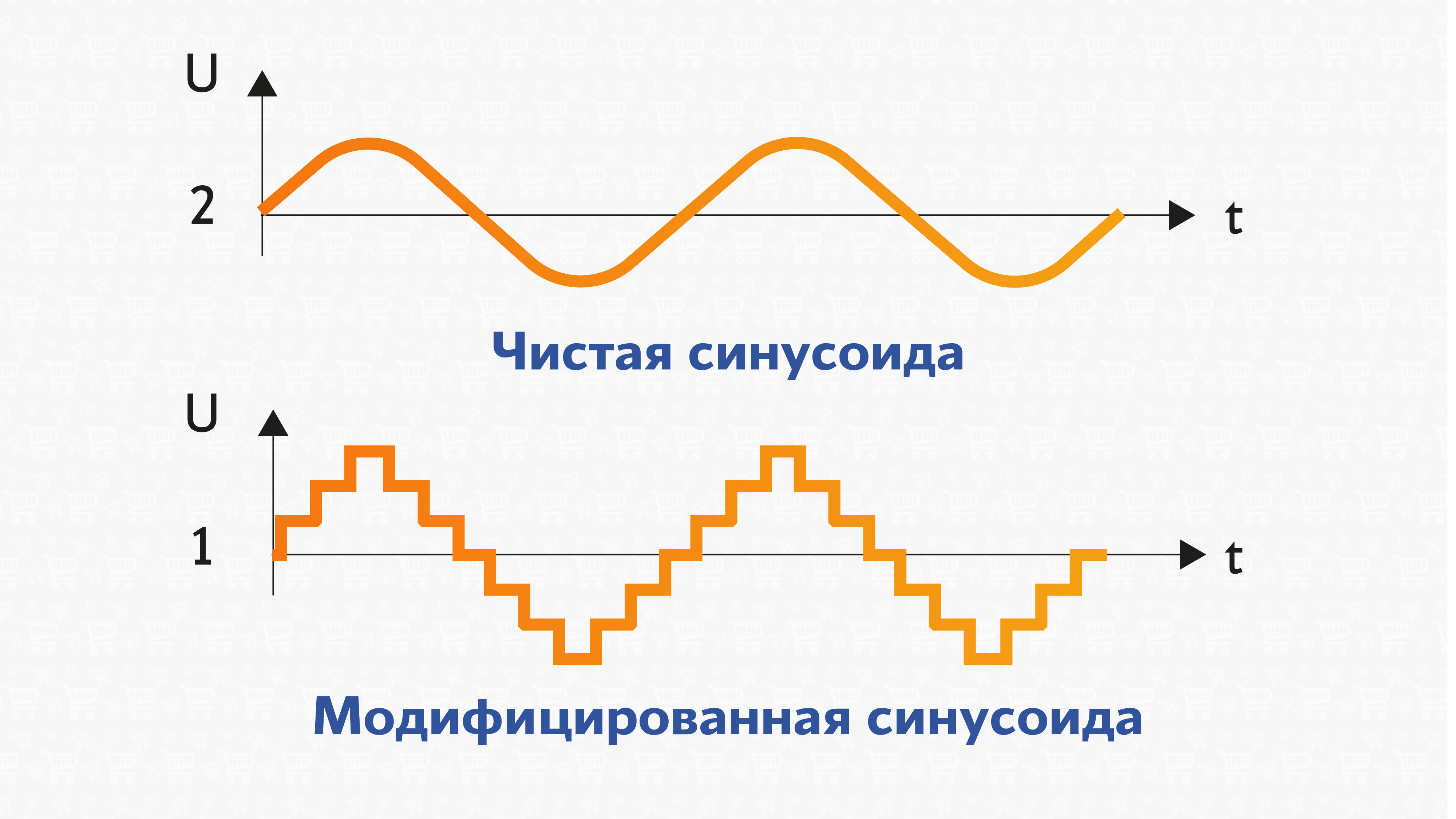 |
| Pure sine wave repeats alternating current, but modified one is still not suitable for the most sensitive consumers. |
- pure sine wave. This is signal with smooth line without jerking, which corresponds to ordinary alternating current. In fact, UPSs with pure sine wave are the most universal, as they are suitable for working with any equipment, including the most sensitive ones - server, medical, heating, all household, etc.;
- similar to sine wave (approximated or modified). This signal, although smoothed to resemble rounded waves, still includes “steps” and jerks. Such UPSs are not suitable for all devices, but, for example, they can be used with computers, as well as with devices that are supplemented with switching power supplies (TVs, monitors, amplifiers).
Pure sine wave is almost mandatory for inverter uninterruptible power supplies, but is sometimes also found in interactive and even backup models. At the same time, this form of voltage, as rule, significantly increases the cost of the UPS.
Autonomy (built-in and plug-in external batteries)
The period of time that you can use devices powered by an uninterruptible power supply during power outage depends on two main points:
- capacity of connected batteries;
- total loads on UPS.
On sale there are both models with batteries included in the delivery set, and with the ability to connect an external battery. In the first case, already upon purchase you can be aware of the battery life. It is usually given under full load conditions. So, if this is an 800 W model, and you connected devices with total of 400 W, then you can count on greater autonomy.
If the battery is initially missing, then it (them) will have to be purchased separately. In this case, you need to independently calculate the operating time during emergency power outages. By the way, you can calculate both the capacity of the required battery, setting the desired period of autonomy, and the backup power time for specific battery. In the latter case, you can use the following formula:
T = (E x V x K) / P, where
T — battery life; E - battery capacity; V - battery voltage; K is the useful capacity coefficient (usually taken as 0.8, less often as 1); P is the power of devices connected to the UPS.
Let's assume you want to connect PC, refrigerator, boiler and minimum set of lighting fixtures (LED). Their total power is 1200 W. You have 100 Ah battery with voltage of 12 V. How long will this set last from the UPS?
T = (100 x 12 x 0.8) / 1200 = 0.8 hours, that is, 48 minutes.
In practice, the battery life will probably be even slightly shorter.
Accordingly, if you know how long the lights are turned off, then you can select the “uninterruptible power supply” capacity that “covers” this period using the formula:
E = (T x P) / (V x K)
To the resulting capacity value, of course, it is worth adding margin of 10 - 20%.
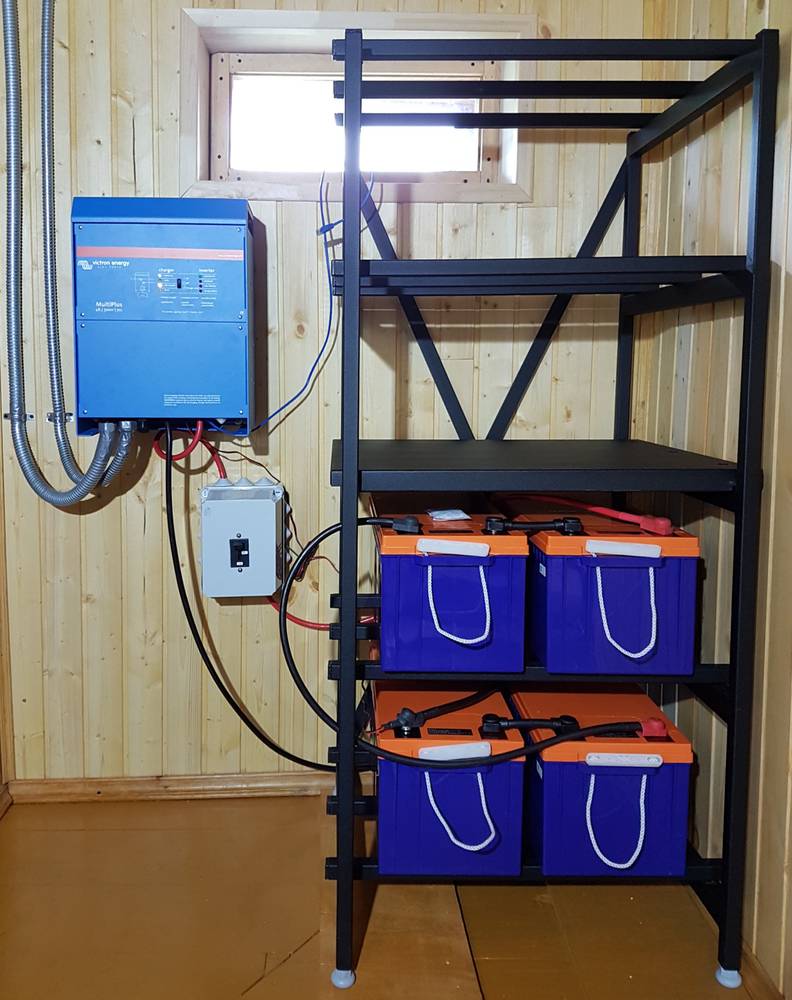
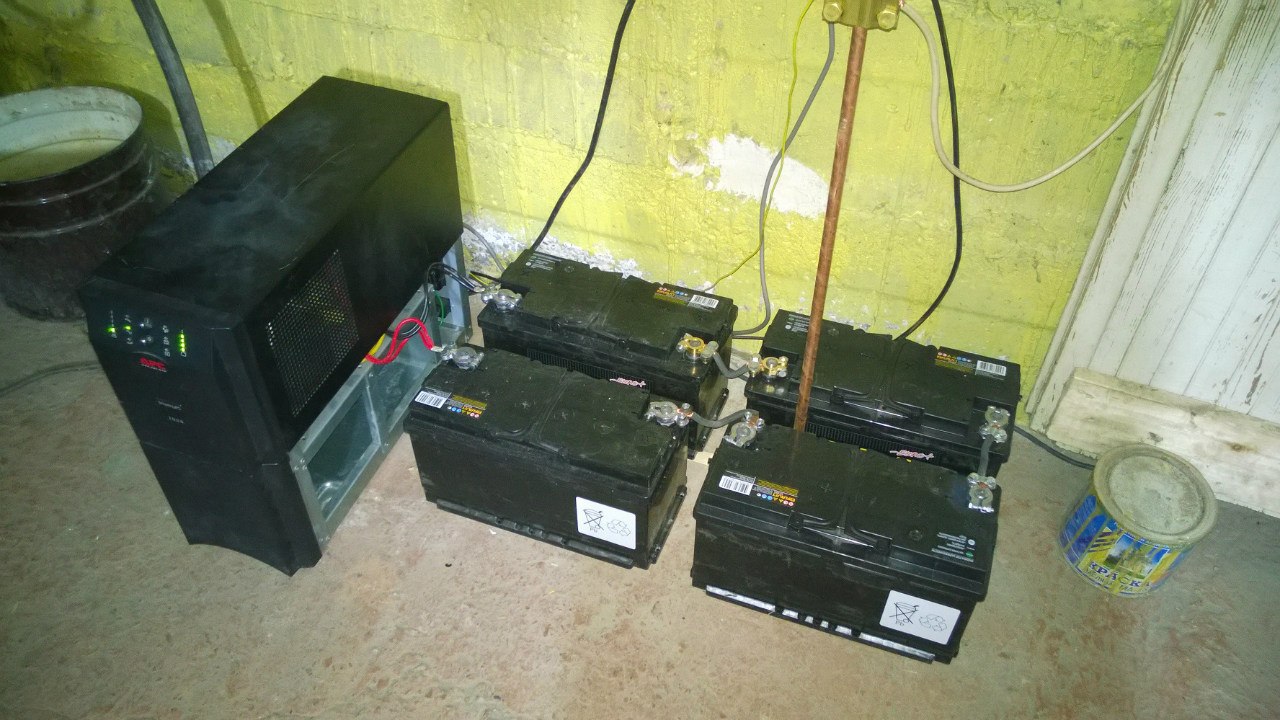 |
| The autonomy of the system directly depends on the number and total capacity of the connected batteries. |
In the case of the ability to connect external batteries, the user can increase the battery life by purchasing several batteries. If there is only built-in battery (without support for external ones), then the replacement process may not be provided at all (or require contacting service centers). Then the user's freedom is significantly limited.
But if UPS is needed only to shut down the PC correctly and turn off running programs, then capacious batteries are not required.
Other important parameters for choosing an uninterruptible power supply
Before purchasing an uninterruptible power supply, you should also consider other points, namely:
- device form factor. Among the most popular are floor-standing models, which can be placed under desktop or almost anywhere else on the floor. In private homes, wall-mounted solutions are in demand, which can be located next to the boiler. Also, low-voltage UPSs are often used in this form factor. For server rooms, the rack option is considered the best choice;
- time to switch to battery. To ensure that the main home appliances do not turn off during power outage, uninterruptible power supplies with an indicator of less than 5 ms are recommended. Moreover, for inverter UPSs this value, with rare exceptions, is zero;
- hot battery replacement. Useful function that makes it possible to change the battery to new one without turning off the uninterruptible power supply. Very popular option for server equipment and security systems;
- number of connectors (interfaces) connection. By default, it should be equal to (or better yet exceed) the number of consuming devices. PCs require IEC 320 C13/C14 sockets, while other household appliances require standard Euro sockets. If there are few of them, you will have to use tees. It is also worth looking first of all at sockets with reserve, that is, connectors that receive power from the battery during power outage. But if there is no reserve, then in case of network failures they will be de-energized, but under normal conditions, interference will be filtered out and voltage surges will be “extinguished.” In addition to sockets, modern UPSs are sometimes supplemented with USB C and USB A ports;
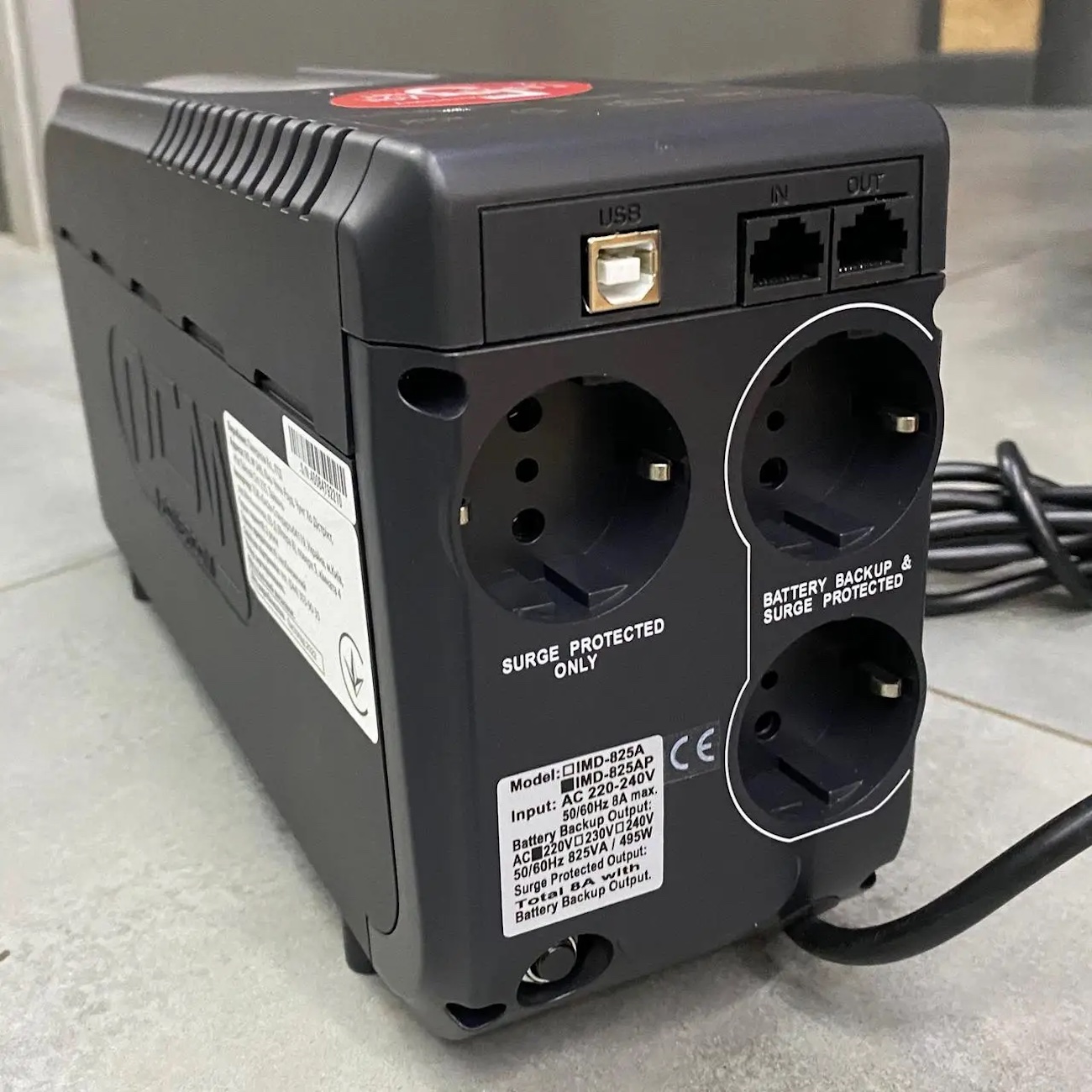 |
| Sockets can be with backup (connected to the battery) or without (only for filtering interference when electricity is available). |
- display and indication. It is easier to learn and use those devices that have clear controls. This could be a display or an additional sound alarm. If we are talking about purchasing UPS for PC, then it is advisable to consider models with condition monitoring software;
- battery charging current. To work with capacious batteries, “uninterruptible power supplies” are recommended, which during the battery charging process can deliver current of 10 A (or better, 20 A). If the current is lower (5 or even 3 A), then the process of replenishing the battery capacity will take a very long time.
In situation with the choice of uninterruptible power supplies, the proverb “measure twice, cut once” works well. It is better to repeat the calculations several times before purchasing and/or additionally consult with specialists, so that later the system works exactly the way you want it.
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials












































































