Power over twisted pair: the essentials of Power over Ethernet

The technology was created for IP telephony, video surveillance systems and other equipment located, for example, in hard-to-reach places or in a zone of shortage of free sockets.
What is it and what equipment supports the technology?
In expanded form, the abbreviation PoE looks like Power over Ethernet, which literally means “power over Ethernet”. The technology was created with an eye on the transmission of electrical energy, along with data, to a remote device through a conventional twisted pair.
Switches, routers and other active network equipment can be assigned to the role of power sources in such networks. The receiving side of the PoE power supply is access points, CCTV cameras, IP phones, all kinds of security and service sensors. There are also intermediate links in the chain that allow active PoE equipment to be connected to devices that do not support the technology. More on that below.
 |
| There are three PoE technology standards. |
In networks with a bandwidth of up to 100 Mbps, data is transmitted only over two pairs of Ethernet cables. Accordingly, the two remaining pairs remain free. According to them, the remote power supply is established in the simplest PoE scheme. In fact, this is not the only option for pinouting the wire - it also depends on the power supply technology standard over the network.
PoE standards
There are three PoE standards in total:
- IEEE 802.3af - the first generation of the standard provides power up to 15.4 W for each consumer;
- IEEE 802.3at (PoE+) - Provides up to 30W of power to each device;
- IEEE 802.3bt (PoE++) - organizes power supply up to 51 W for each. In this case, all eight conductors of the twisted pair are involved in the work.
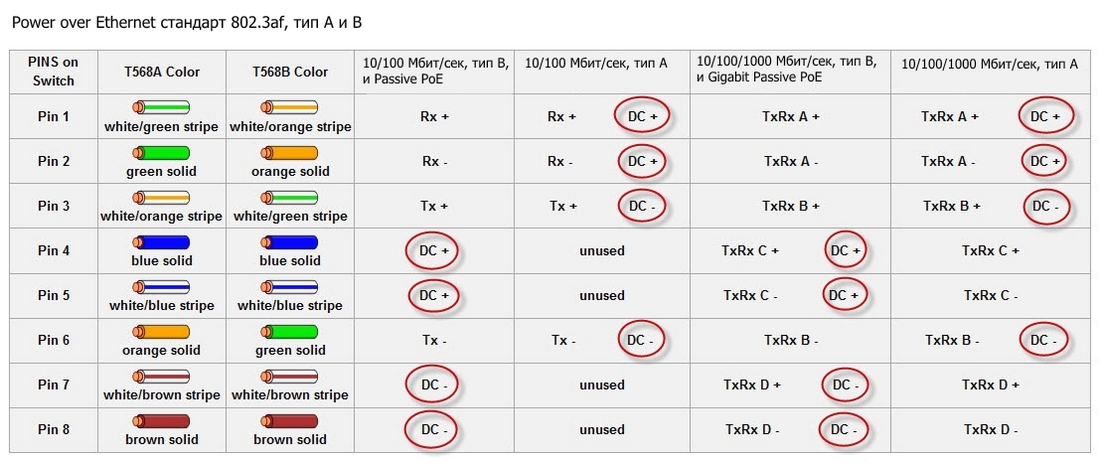
For the first IEEE 802.3af standard, type A and type B pinouts are provided:
- Type A - the transmission of electricity and data is established through cores 1, 2, 3, 6. Cores with serial numbers 4, 5, 7, 8 are not used.
- Type B - conductors 4, 5, 7, 8 are used to supply electrical power. Data is transmitted through the rest.
 |
| Variations of Ethernet wire pinout schemes. |
In the second IEEE 802.3at (PoE+) standard, only scheme B is used. Visual differences between PoE standards can be seen in the table:
| Characteristics | PoE | PoE+ | PoE++ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Powered Device DC Voltage (V) | 36-57 | 42.5-57 | 41.1-57 |
| Source voltage (V) | 44-57 | 50-57 | 52-57 |
| Maximum PoE Source Power (W) | 15.4 | thirty | 90 |
| Maximum power received by the consumer (W) | 12.95 | 25.5 | 71.3 |
| Maximum current (mA) | 350 | 600 | 960 |
| Maximum Cable Resistance (Ohm) | 20 (for cat.3) | 12.5 (for cat.5) | 12.5 (for cat.5) |
| Food classes | 0-3 | 0-4 | 0-8 |
In addition , each powered device is assigned a specific class from 0 to 4, depending on the level of power consumption. This is necessary for further power management.
| Class | W per PoE port | watts per device |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 15.4 | from 0.44 to 12.95 |
| one | 4.5 | from 0.44 to 3.84 |
| 2 | 7 | from 3.84 to 6.49 |
| 3 | 15.4 | from 6.49 to 12.95 |
| four | thirty | from 12.95 to 25.5 |
The network device supplies power to consumers only if the connected equipment supports PoE technology. At the first stage, the powered device is checked, during which a voltage from 2.8 to 10 V is applied to it and the input resistance is determined. If the parameters correspond to the required ones, the supply equipment proceeds to the definition of the above classes. After passing through the stages of definition and classification, the power supply device supplies the cable with a voltage of 48 V with a rising front no faster than 400 ms.
PoE intermediate equipment
If it is necessary to include equipment in the network infrastructure that does not support power over twisted pair, Passive PoE technology is used. Its integral link is a PoE splitter, which separates the signal incoming over the wire into data and power (12 V-24 V). The power indicators in such a scheme will have to be coordinated independently, carefully checking the correspondence between the characteristics of the source and the consumer.
There is also a reverse situation when a client device with PoE needs to be connected to network equipment without this technology. In such a scheme, one cannot do without a PoE injector, which has an RJ45 port at the input and a connector for connecting to a power source. At the output, it has the only RJ45 connector already with PoE.
 |
| A visual representation of a PoE circuit with an injector and a splitter. |
Intermediate links in the PoE power scheme are referred to as Mid-span. Well, devices that supply power from the beginning of the cable line are called End-span.
Cable Requirements
A separate package of requirements is provided for the cable to deploy PoE schemes. They must use twisted-pair category 5e or higher. In this case, copper conductors are needed, and not just copper-plated ones. Their thickness must be at least 0.51 mm, and the resistance must not exceed 9.38 ohm/100 m.
 |
| Twisted pair for PoE systems has a special set of requirements. |
The maximum transmission range of PoE power over twisted pair rests on the 100-meter threshold, which is prescribed in the requirements of the 802.3af and 802.3at standards. However, in practice it is desirable to use cables up to 75 m in the case of End-span equipment and up to 60 m in Mid-span circuits. Some advanced switches feed consumers over twisted pair and at a distance of up to 250 m. A vivid example of this is the ZyXel GS1350-18HP switch, which is a specialist for ensuring the performance of video surveillance systems.
Technology Benefits
The key advantages of PoE technology can be highlighted in separate points:
- Connecting powered devices in hard-to-reach places.
- Power management(relevant "remotely" when you need to restart frozen equipment or devices after the "arrival" of a package of fresh updates).
- Electrical safety(for PoE, the maximum voltage is 57 V).
- Simplification of maintenance(technicians will have to tinker with the circuit less in case of malfunctions).
- The aesthetic side of the issue(the absence of extra wires will be appreciated by perfectionists).
The technology also has disadvantages: the higher cost of network equipment, the notorious power drop over long distances of power transmission, the requirements for the necessary qualifications of maintenance personnel.
The beauty of Power over Ethernet is that it uses the same set of wires for data and power. As a result, the installation of systems powered by twisted pair is greatly simplified and it is possible to achieve cost savings on the cost of power cables and other components of the deployed network.
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials




































































